Note:
|
Variables |
Descriptions |
|
1-£\ |
Two-sided confidence level |
|
p |
Success proportion in sample |
|
x |
Number of success in sample |
|
n |
Sample size |
|
Lower |
Lower C.I. |
|
Upper |
Upper C.I. |
Help Aids Top
Procedure:
- Enter
a) Value of 1-£\, the two-sided confidence level
b) Value of p, the success proportion in sample
c) Value of x, the number of success in sample
d) Value of n, the sample size
Note that either x or p must be entered. If either one of them is unknown, enter "null" in the box.
- Click the button ¡§Calculate¡¨ to obtain the lower and upper endpoints of 100(1-£\)% confidence interval
- Click the button ¡§Reset¡¨ for another new calculation
Formula:
If p is unknown, ![]()
Define: ![]()
The 100(1-£\)% Wilson Score confidence interval with continuity correction is defined as:
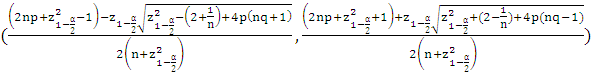
Notation:
100(1-£\)% confidence interval: We are 100(1-£\)% confident that the true value of the parameter is included in the confidence interval
![]() : The z-value for
standard normal distribution with left-tail probability
: The z-value for
standard normal distribution with left-tail probability![]()
Examples Top
Suppose the response rate of the patient population under study after treatment is expected to be around 13.3333% (p=0.133333, x=null).
The 95% confidence interval ((1-£\) =0.95) with sample size 30 (n=30) is (0.043597, 0.316424).
The drug Minoxidil was approved by the FDA as an antihypertensive drug in heart disease patients. An unexpected side effect of the topical form of the drug was hair growth. A study was conducted and this drug was administered to 95 balding men and 43 of them experienced hair growth. Compute and interpret a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of bald men who respond to Minoxidil.
The 95% C.I. (1-£\=0.95, n=95, x=43) is (0.35, 0.56). We are 95% confident that the true proportion of bald men who would respond to topical Minoxidil is between 0.35 and 0.56.